The key difference between these two structural components is the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
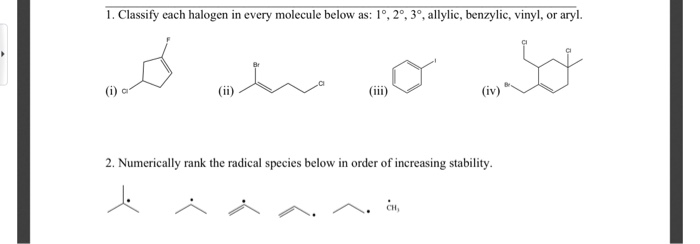
Allylic vs benzylic or vinylic.
Benzylic position allylic position propargylic position aryl aryl hydrogen methyl hydrogen primary hydrogen secondary hydrogen tertiary.
Vinyl group has two carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms.
Carbo cations may be stabilized by.
Vinylic carbocations are unstable as they lack p character.
Allyl form a stable carbocation because of the electron delocalization.
Vinyl group vinylic hydrogen vinylic carbocation allylic position benzylic position propargylic position wikipedia entry return to glossary index.
But would the c bound to the 2 carbons in a double bond also be considered an allylic carbon.
For 3º halides a very slow s n 2 substitution or if the nucleophile is moderately basic e2 elimination.
Allyl group holds three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms.
Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule.
Benzene c x where x is the benzylic group vinylic.
The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon.
Key difference allyl vs vinyl both allyl and vinyl groups have slightly similar structures with a small variation.
Both groups own a double bond between two carbon atoms where all the other atoms are bonded through single bonds.
Allyl groups have three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms.
I have heard about allylic vinylic benzylic carbons but positions.
Would x in c c x be vinylic on the same train of thought claisen rearrangements utilize vinylic allyl ethers.
In high dielectric ionizing solvents such as water dimethyl sulfoxide acetonitrile s n 1 and e1 products may be observed.
The vinylic hydrogens are shown in red.
A π bonds only at allylic position b π bonds only at vinylic position c π bonds at allylic and benzylic position also d i effect while the answer is obviously not d i am really confused about what allylic vinylic and benzylic positions actually mean.
Allyl h 2 c chch 2 rapid s n 2 substitution for 1º and 2º halides.
An allylic hydrogen is a hydrogen atom that is bonded to an allylic carbon in an organic molecule.
So x in c c c x would be an allylic group.
None of the other hydrogens are vinylic.